The Critical Path Method can be used to optimize the flow and efficiency of a project's schedule. This method is helpful for projects in which even one delay could affect project performance. The Critical Path Method is a way to optimize the flow and quality of your project. The following example will show how this technique is useful to an airline company: Imagine airline company A has a limited number of flights and low profitability. Management may decide increase daily utilization to 10 hours per aircraft to increase profitability. This could lead to an additional $100,000 per aircraft each year. This strategy could also be applied to other flights and require fewer airplanes.
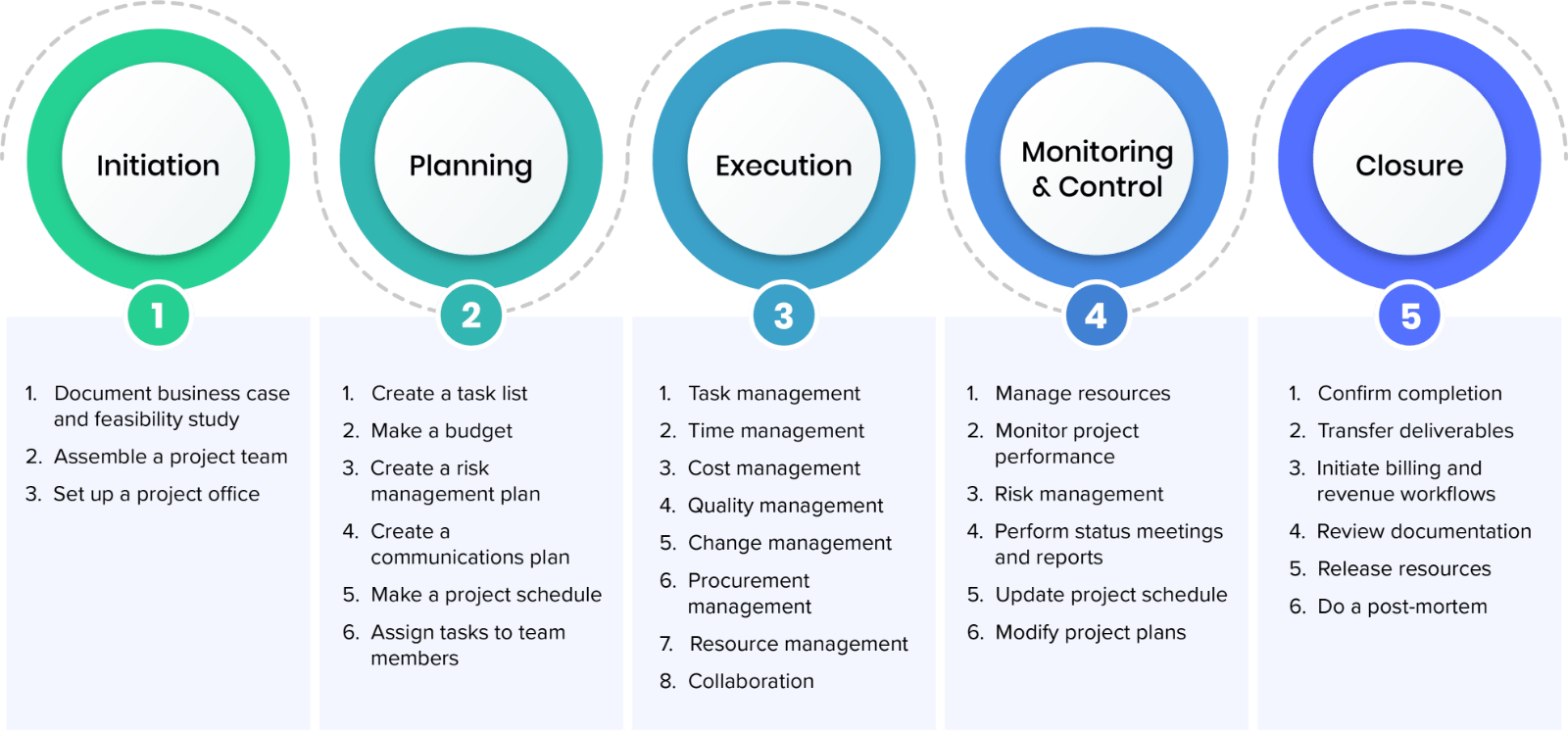
Management of projects
The Critical Path Method can be used to help you visualise the goals of your project and prioritize tasks to accomplish them. A sequence of activities must be completed in order to complete the project on time. This technique is often used to manage projects and is often used together with a review and program evaluation. It is an excellent tool for estimating the duration of a project and can help you determine resource allocation, activity scheduling, and risk.
The Critical Path Method for Project Management helps you to make a detailed schedule. This is done by identifying the tasks and activities that are essential to the project's success. It can help you monitor stakeholder expectations, keep track of progress, and monitor your stakeholders' expectations. It allows you to adjust the timetable to meet the project's deadlines, and helps you achieve your project goals quicker. You can also use the Critical Path Method to help you plan for time for individual team members.

Schedule analysis
The Critical path method is a common way to analyze a project's schedule. This method utilizes a series of formulas to estimate how much time is necessary for each activity on a schedule. This method is particularly useful in projects where every activity is crucial to the success or failure of the project. Each activity has a maximum duration and a minimum duration. These dates can be used to help you plan and make adjustments.
The Critical Path method starts with identifying the points where each activity can begin or end. This information is useful for planning and implementing delays and creating a project plan. Example: Job A with an EST 10 is considered critical. Similarly, if job d has an EST of 30, it is considered critical. Once all the tasks have a critical path, the total duration of the project can be calculated.
Gantt chart
The critical path method is essential for project scheduling. Henry Gantt's Gantt chart is a powerful tool. It shows the entire project from start to finish and allows project managers to easily see the most crucial activities. This type of chart is particularly useful for construction projects, but can also be used for traditional project management. It encourages collaboration.
To monitor progress at different milestones and phases, a Gantt chart can be used with a critical path. One critical path can be broken into multiple critical paths. Each of these can have different dependencies. This chart can show all tasks in the project. It is especially useful for teams that are working together on one task. Multiple critical paths can be beneficial in some cases to make the project easier to manage.

Calculate the floating point
The critical path is a method to estimate a project's total duration and critical activities. The critical path can be described as a continuous chain or sequence of critical actions. The sum of the durations of these activities equals the overall project duration. If one of the crucial activities is delayed, the entire project will be halted. One critical path may be part of a project. For calculating the float of your project, you will need to know each activity's critical path duration.
Free floating calculations can be performed manually or with project management software. Software packages can automatically calculate metrics like slippage or critical paths. By following the float paths of each task, you can calculate float. This method can be used to calculate the float for both your entire project and for each task individually. However, you should use the critical path method with caution as it can lead to inaccurate results.
FAQ
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma uses statistical analyses to locate problems, measure them, analyze root cause, fix problems and learn from the experience.
First, identify the problem.
The data is then analyzed and collected to identify trends.
The problem can then be fixed by taking corrective measures.
Final analysis of data is done to determine if the problem has been solved.
This continues until the problem has been solved.
It can sometimes seem difficult to make business decisions.
Complex systems with many moving parts are the hallmark of businesses. They require people to manage multiple priorities and deal with uncertainty and complexity.
It is important to understand the effects of these factors on the system in order to make informed decisions.
This requires you to think about the purpose and function of each component. It is important to then consider how the individual pieces relate to each other.
You need to ask yourself if your previous actions have led you to make unfounded assumptions. If so, it might be worth reexamining them.
Asking for assistance from someone else is a good idea if you are still having trouble. They might see things differently than you and may have some insights that could help find a solution.
Why is project management so important?
Project management techniques ensure that projects run smoothly while meeting deadlines.
Because most businesses depend heavily on project work to produce goods or services,
Companies must manage these projects effectively and efficiently.
Companies that do not manage their projects effectively risk losing time, money, or reputation.
Statistics
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
External Links
How To
How does Lean Manufacturing work?
Lean Manufacturing processes are used to reduce waste and improve efficiency through structured methods. These processes were created by Toyota Motor Corporation, Japan in the 1980s. The main goal was to produce products at lower costs while maintaining quality. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating unnecessary steps and activities from the production process. It is composed of five fundamental elements: continuous improvement; pull systems, continuous improvements, just-in–time, kaizen, continuous change, and 5S. Pull systems involve producing only what the customer wants without any extra work. Continuous improvement involves constantly improving upon existing processes. Just-in-time is when components and other materials are delivered at their destination in a timely manner. Kaizen means continuous improvement, which is achieved by implementing small changes continuously. Last but not least, 5S is for sort. These five elements are used together to ensure the best possible results.
The Lean Production System
Six key concepts make up the lean manufacturing system.
-
Flow - focus on moving material and information as close to customers as possible;
-
Value stream mapping - Break down each stage in a process into distinct tasks and create an overview of the whole process.
-
Five S's – Sort, Put In Order Shine, Standardize and Sustain
-
Kanban: Use visual signals such stickers, colored tape, or any other visual cues, to keep track your inventory.
-
Theory of constraints: identify bottlenecks in your process and eliminate them using lean tools, such as kanban board.
-
Just-in-time delivery - Deliver components and materials right to your point of use.
-
Continuous improvement is making incremental improvements to your process, rather than trying to overhaul it all at once.