The right place to look if you want to improve the digital media supply chain workflow is here. We will be looking at the challenges and trends that face the media industry today and offering some solutions. No matter the size of your business, it is important to be aware of the trends and challenges that face the media supply chains. These workflows will eventually improve your bottomline and help meet your content marketing goals.
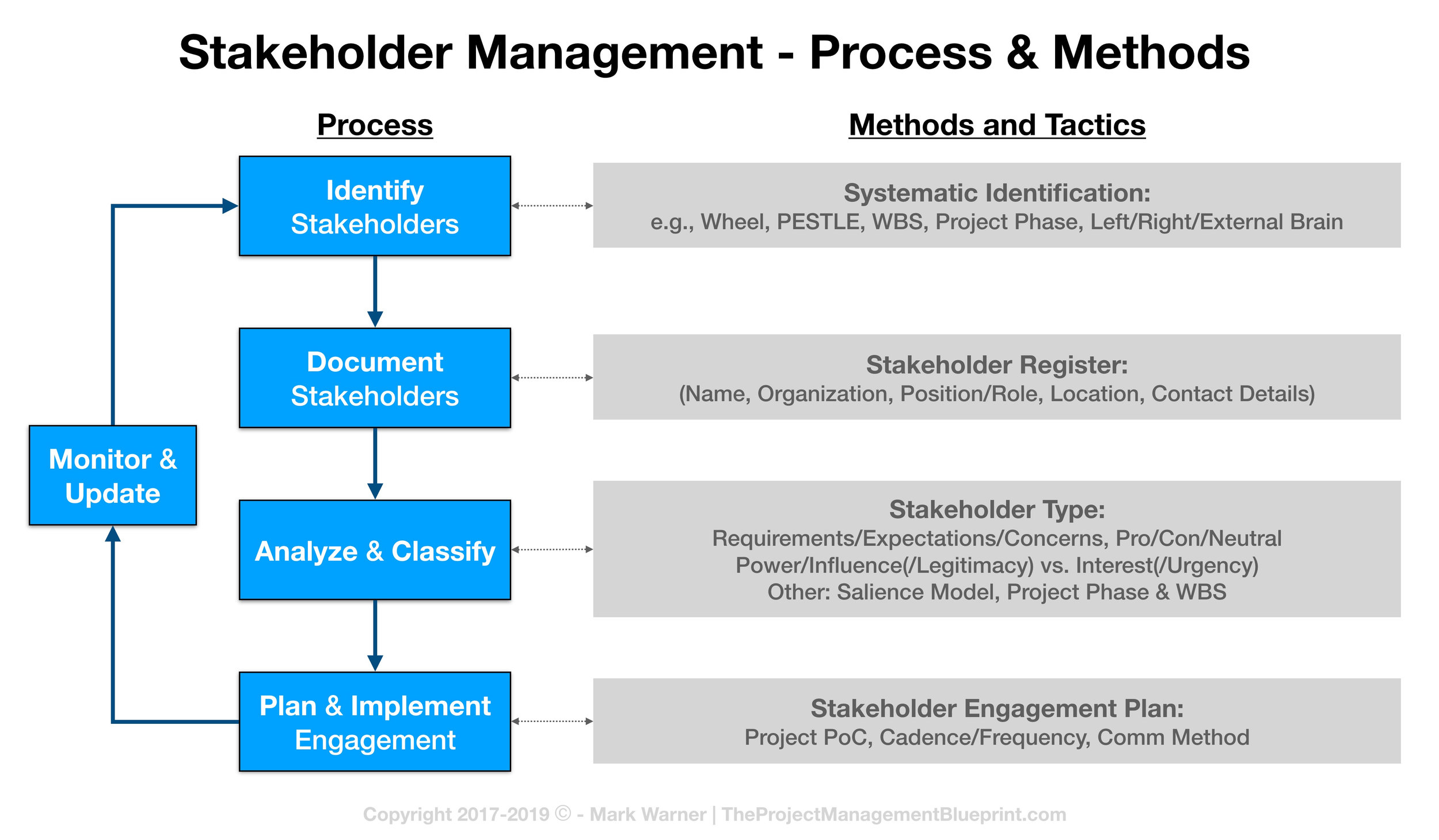
Digital media supply chain
A digital media supply network is a collection of processes to manage media files as well as their metadata. The use of media asset management systems (MAM) has been around since the beginning of TV, movies, and video production. Technology is an important tool for many organizations. From production to distribution, the supply chain needs to manage all files during the production and postproduction stages.
There are many components to the digital media supply chains, including content delivery networks and content management system. Each component of a digital media supply network should be capable of being integrated with the other components, and can leverage automation and artificial Intelligence to meet the company's needs. The digital media supply chain is a dynamic marketplace, and the technologies employed must be flexible enough to keep pace with the ever-changing demands of the market.
Challenges
A lack of standardization is often at the root of the challenges in media supply chain workflow. It is crucial to create standard processes and systems, as consumers expect content to be available from all devices. This will enable companies to manage an ever increasing number of content. This requires companies to work to make the workflow more efficient and effective. There are several options for automating the workflow. However, there are risks associated with these solutions.
The four major dimensions of supply chain challenges can be divided into operational, behavioural and financial. This method allows managers to focus on the issues relevant to their businesses. If a country has a "protectionism” policy, it will reduce the supply chain. Businesses will need to spend more time on paperwork and crossing borders. Final, companies may have to wait longer for goods from distant suppliers.
Solutions
A media workflow is a way to automate production, simplify storage, and meet service-level expectations. The use case for such a workflow describes the lifecycle of media assets, the management of data, and the processes involved in the production. Diversified works together with clients to identify the use cases and prioritize their goals. This helps to design a successful system. The company developed an innovative media workflow solution.
The media supply chain is a digital process that includes creation, management, and delivery of digital media. It is therefore important that the workflow used in this process be flexible, customizable, and adaptable. It should also support different user interfaces and application contexts. The technology must be able to support different media assets and provide specific functionality. A media supply chain solution must support multiple formats and devices, in particular.

Trends
As new approaches and technologies are developed, the media supply chains continue to change. Content creators are going to be more concerned about consistency and performance. The recent pandemic brought new challenges to broadcasters and the media supply network. Automation technology will allow companies to streamline their workflow and create a self -healing supply network. These advancements come with their own risks. You can learn more about trends in the media supply chain workflow and how to ensure that your content is delivered within budget.
For today's digital world, traditional supply chains no longer work. Consumers want access to the most recent technology and high-quality content. Media organizations need to transform media supply chains in order for them to be able meet consumer demand. These problems can be solved by cloud-based technologies. Media companies without cloud solutions might not be as agile in meeting global audiences' needs and have higher delivery costs. In addition, their workflow may not be meeting consumer needs.
FAQ
What are the main styles of management?
These are the three most common management styles: participative (authoritarian), laissez-faire (leavez-faire), and authoritarian. Each style has its advantages and disadvantages. Which style do you prefer? Why?
Authoritarian - The leader sets the direction and expects everyone to comply with it. This style works best in large organizations that are stable and well-organized.
Laissez-faire: The leader lets each person decide for themselves. This style is most effective when the organization's size and dynamics are small.
Participative - Leaders listen to all ideas and suggestions. This style is most effective in smaller organizations, where everyone feels valued.
What do we mean when we say "project management"?
We mean managing the activities involved in carrying out a project.
This includes defining the scope, identifying the requirements and preparing the budget. We also organize the project team, schedule the work, monitor progress, evaluate results, and close the project.
What is Six Sigma?
It's a strategy for quality improvement that emphasizes customer care and continuous learning. This is an approach to quality improvement that uses statistical techniques to eliminate defects.
Motorola created Six Sigma as part of their efforts to improve manufacturing processes in 1986.
The idea spread quickly throughout the industry, and today, many organizations are using six sigma methods to improve product design, production, delivery, and customer service.
Statistics
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
External Links
How To
How can Lean Manufacturing be done?
Lean Manufacturing techniques are used to reduce waste while increasing efficiency by using structured methods. These processes were created by Toyota Motor Corporation, Japan in the 1980s. The primary goal was to make products with lower costs and maintain high quality. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating redundant steps and activities from the manufacturing process. It is composed of five fundamental elements: continuous improvement; pull systems, continuous improvements, just-in–time, kaizen, continuous change, and 5S. Pull systems are able to produce exactly what the customer requires without extra work. Continuous improvement is constantly improving upon existing processes. Just-in-time is when components and other materials are delivered at their destination in a timely manner. Kaizen means continuous improvement, which is achieved by implementing small changes continuously. Finally, 5S stands for sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. These five elements can be combined to achieve the best possible results.
Lean Production System
Six key concepts make up the lean manufacturing system.
-
Flow - focus on moving material and information as close to customers as possible;
-
Value stream mapping- This allows you to break down each step of a process and create a flowchart detailing the entire process.
-
Five S's: Sort, Shine Standardize, Sustain, Set In Order, Shine and Shine
-
Kanban: Use visual signals such stickers, colored tape, or any other visual cues, to keep track your inventory.
-
Theory of constraints - identify bottlenecks during the process and eliminate them with lean tools like Kanban boards.
-
Just-in Time - Send components and material directly to the point-of-use;
-
Continuous improvement - make incremental improvements to the process rather than overhauling it all at once.