
Workers are protected against dangers by the hierarchy of control. It is widely used in many industries. It is taught to all industry managers and accepted as a standard practice. However, there are some variations of this system. Check out this guide to the NFPA70E hazard rating system and the ARECC variation. This information will help you to better apply the hierarchy in your workplace.
NFPA 70E
NFPA70E is a set standard for electrical safety at work. In the 2018 edition, there is an Annex Q section. This describes human performance and human errors and their potential adverse consequences. This section includes a hierarchy that prioritizes the elimination and prevention of hazards. In the case of electrical hazards, eliminating the source of energy or hazard is the first step. Personal protective gear should only be used in extreme cases.
Next is to determine the degree of exposure to hazards. Then, you will need to decide on the most appropriate engineering controls that can reduce the severity. While engineering controls may reduce the danger from hazardous substances, they do not eliminate it completely. The hierarchy of control's goal is to reduce the severity of hazards and prevent them from happening. An example of engineering control is a fog or vapor machine, ventilation system or fire alarm.
Appendices to the NFPA70E standard are also available. These appendices are documents that provide detailed instructions and guidelines on how to perform specific procedures. Appendices contain sample forms, PPE guidance and design requirements as well as risk assessment guidelines. As with the main text, the annexes are meant to provide guidance on how to implement the standard. They can provide information that may prove helpful in ensuring the safety and security of buildings or workplaces.
ARECC Variation
The ARECC variation is a way to reduce exposure to a particular hazard. This system is traditionally used in the United States and Canada, but it has been adapted in other countries. For example, some countries place isolation before engineering controls, while others combine both. The ARECC variant includes employee training and warnings. Important to understand that warnings can't eliminate all hazards from a workplace.
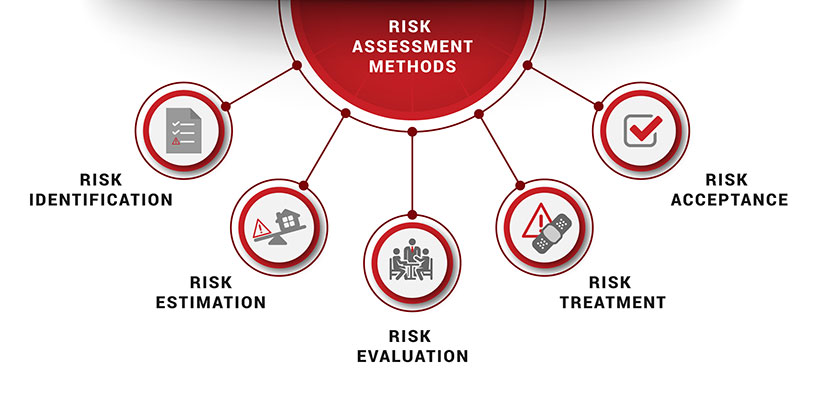
The ARECC hierarchy is a system for occupational safety and protection. It provides a framework for occupational safety and health. The hierarchy contains five categories of controls: engineering controls and administrative controls. Each category has unique strengths and weaknesses. They are all important for specific situations. Some controls included in the ARECC hierarchy may be more effective than others.
FAQ
What are some common management mistakes?
Managers sometimes make their own job harder than necessary.
They may not be able to delegate enough responsibility to staff or provide adequate support.
In addition, many managers lack the communication skills required to motivate and lead their teams.
Managers set unrealistic expectations and make it difficult for their team.
Managers may choose to solve every problem all by themselves, instead of delegating to others.
What is the main difference between Six Sigma Six Sigma TQM and Six Sigma Six Sigma?
The main difference between these two quality management tools is that six sigma focuses on eliminating defects while total quality management (TQM) focuses on improving processes and reducing costs.
Six Sigma is an approach for continuous improvement. It emphasizes the elimination of defects by using statistical methods such as control charts, p-charts, and Pareto analysis.
This method aims to reduce variation in product production. This is accomplished through identifying and correcting root causes.
Total Quality Management involves monitoring and measuring every aspect of the organization. It also includes training employees to improve performance.
It is often used to increase productivity.
What are the steps of the management decision-making process?
Managers face complex and multifaceted decision-making challenges. It involves many elements, including analysis, strategy. planning. implementation. measurement. evaluation. feedback.
The key thing to remember when managing people is that they are human beings just as you are and therefore make mistakes. You are always capable of improving yourself, and there's always room for improvement.
This video shows you how management makes decisions. We'll discuss the different types and reasons they are important. Managers should also know how to navigate them. These topics are covered in this course:
What is Kaizen, exactly?
Kaizen is a Japanese term meaning "continuous improvement." It is a philosophy that encourages employees to constantly look for ways to improve their work environment.
Kaizen is based on the belief that every person should be able to do his or her job well.
How does a manager develop his/her management skills?
It is important to have good management skills.
Managers must monitor the performance of subordinates constantly.
If you notice your subordinate isn't performing up to par, you must take action quickly.
You should be able pinpoint what needs to improve and how to fix it.
What is TQM?
When manufacturing companies realized that price was not enough to compete, the industrial revolution brought about the quality movement. To remain competitive, they had to improve quality as well as efficiency.
Management developed Total Quality Management to address the need for improvement. It focused on all aspects of an organisation's performance. It included continuous improvement and employee involvement as well as customer satisfaction.
Statistics
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
QMP (Quality Management Plan), introduced in ISO 9001,2008, provides a systematic method for improving processes, products, or services through continuous improvement. It focuses on the ability to measure, analyze and control processes and customer satisfaction.
QMP stands for Quality Management Process. It is used to guarantee good business performance. QMP is a standard method that improves the production process, service delivery, customer relationship, and overall business performance. QMPs should cover all three dimensions - Products, Processes, and Services. If the QMP focuses on one aspect, it is called "Process." QMP. QMPs that focus on a Product/Service are known as "Product" QMPs. If the QMP focuses on Customer Relationships, it's called a "Product" QMP.
When implementing a QMP, there are two main elements: Scope and Strategy. They are defined as follows:
Scope: This determines the scope and duration of the QMP. This will be used to define activities that are performed in the first six months of a QMP.
Strategy: This is the description of the steps taken to achieve goals.
A typical QMP has five phases: Planning (Design, Development), Implementation (Implementation), and Maintenance. Each phase is described below:
Planning: In this stage the QMP's objectives and priorities are established. Every stakeholder involved in the project is consulted to determine their expectations and needs. The next step is to create the strategy for achieving those objectives.
Design: This stage is where the design team creates the vision, mission and strategies necessary for successful implementation of QMP. These strategies are put into action by developing detailed plans and procedures.
Development: Here, the development team works towards building the necessary capabilities and resources to support the implementation of the QMP successfully.
Implementation: This involves the actual implementation of the QMP using the planned strategies.
Maintenance: It is an ongoing process that maintains the QMP over time.
The QMP must also include several other items:
Stakeholder involvement is important for the QMP's success. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
Project Initiation: It is essential to have a clear understanding about the problem and the solution before you can initiate a project. This means that the initiator should know why they want something done and what they hope for from the end result.
Time Frame: This is a critical aspect of the QMP. If you plan to implement the QMP for a short period, you can start with a simple version. If you're looking to implement the QMP over a longer period of time, you may need more detailed versions.
Cost Estimation: Another important component of the QMP is cost estimation. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. Therefore, cost estimation is essential before starting the QMP.
QMPs should not be considered a static document. It is constantly changing as the company changes. It is important to review it periodically to ensure it meets all current requirements.